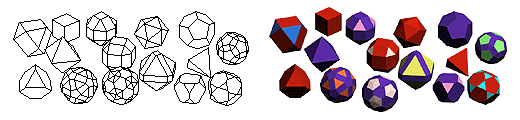|
|
|
AutoDesSys products: |
|||||
|
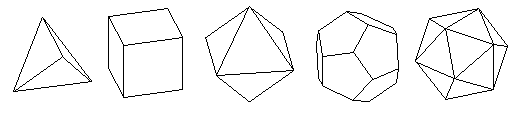
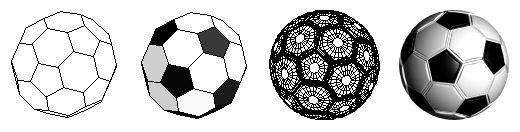
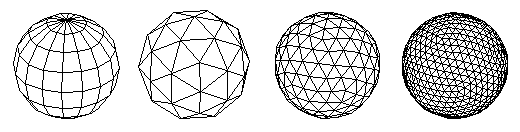
Spherical objects: Platonic solids, soccer balls, lathed and geodesic spheres The unique spherical objects that form·Z can create consist of the complete set of Platonic solids, the soccer ball, and both lathed and geodesic spheres. All the spherical objects can be derived directly in 3D space with a few clicks of the mouse, and can be scaled and stretched as they are created, which allows the creation of elliptical forms. The classical Platonic solids are symmetrically "perfect" forms that consist of equal polygonal faces. These Platonic solids can be further manipulated using other tools in form·Z, such as beveling the corner points or edges, to create another vast group of symmetrically spherical objects. The Platonic solids. Above, left to right: Tetrahedron, hexahedron, octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron. Below: After beveling points or edges of platonic solids a variety of spherical forms can be derived. The soccer ball is a derivative of two Platonic forms and consists of equal pentagons and hexagons. The faceted faces of the basic soccer ball can be further articulated using other form·Z tools to smoothly round its surfaces, for a more realistic appearance, when it is viewed at a larger scale.
|
|
|
|||