|
|
|
AutoDesSys products: |
|||||
|
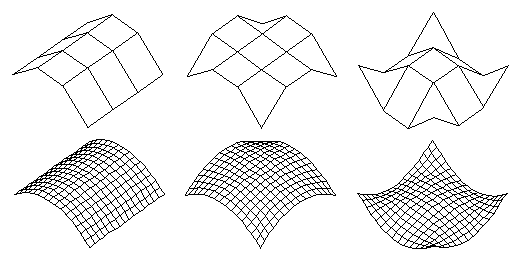
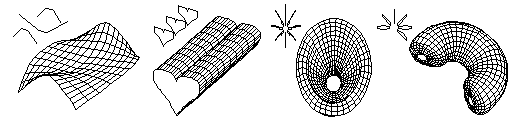
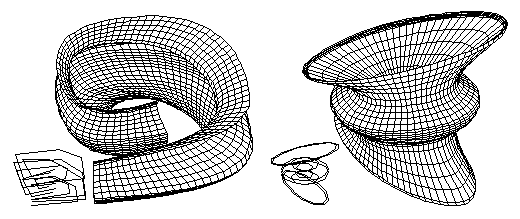
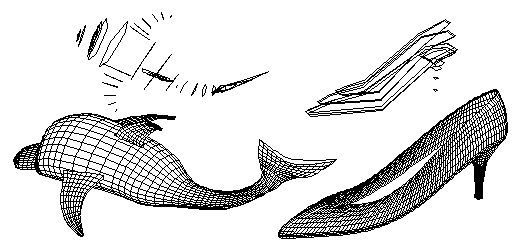
C-meshes The complete range of curved lines (splines), including NURBS, can also be used in a 3D arrangement to produce curved surfaces called controlled meshes or c-meshes. These objects are stored with their control parameters, and can thus be edited later, through interactive graphic procedures, to change their shapes. The c-meshes can be either surface or solid objects. When solid, their ends can be rounded, or they can be closed to produce a ring-like object. Above: Three control nets and the c-meshes they generate. Below, left to right: A surface c-mesh, a solid c-mesh, a ring-like c-mesh, and a solid c-mesh with rounded ends. The variety of 3D forms that can be created with c-meshes is virtually unlimited. Four examples and the control lines from which they were generated are shown below.
|
|
|
|||