|
|
|
AutoDesSys products: |
|||||
|
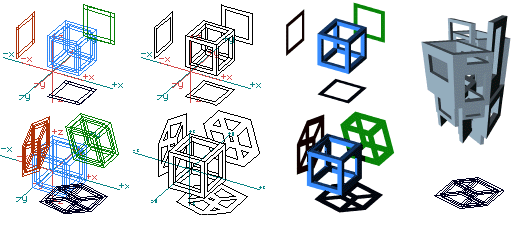
Projection objects Two dimensional objects can be derived from either the orthographic projections or the projected 3D views of other objects positioned anywhere in 3D space. This unique operation of form·Z, which is executed with a single click of the mouse, can be useful for a variety of practical applications, as well as for design explorations relating to perceptual investigations. After their generation, the 2D projection shapes can be used to derive other 3D objects, as shown in the example to the right below.
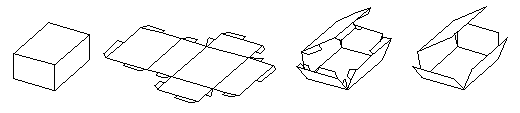
Top row: Deriving objects from orthographic projections. Bottom row: Deriving objects from the projections of 3D views. Right: Projection shapes can be used to derive other 3D objects. Even more unique are the unfolded projections of 3D objects that form·Z is capable of deriving from any form, including shapes that contain holes. The pattern in which an object will be unfolded can be controlled by clicking on the segment where the unfolding will start. That is, for most objects, different unfolded patterns will be derived if you click on different segments to select the object. The unfolded pattern can also be regulated by breaking an object into parts before unfolding it.
Three solid objects unfolded.
Left to right : A cuboid, unfolded with connectors. Refolding the cube with and without connectors.
|
|
|
|||