|
|
|
AutoDesSys products: |
|||||
|
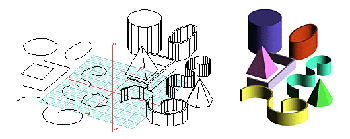
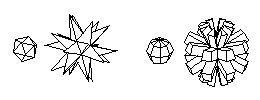
Derivative 2D shapes and 3D forms Objects can be derived from other previously created 2D or 3D objects. This unique ability of form·Z offers a vast variety of methods for synthesizing 3D forms.
Three dimensional extrusions, parallel to the surface, or converging to a point, can also be derived from any surface of a previously created object. Likewise, enclosures, which are double line or double surface objects, also known as "walls", can be created from surfaces of other objects. These extrusions can be perpendicular to the surface of the extruded shape or in any direction determined by the active reference plane. Both cases are illustrated below.
|
|
|
|||